ウィルス分布 学習
TensorBoardに表示するグラフをリセットし、TensorFlowの変数とプレースフォルダを定義する。

ロジスティック回帰のモデルを定義する。y = x * w + b

コストの定義をする。

精度の定義をする。

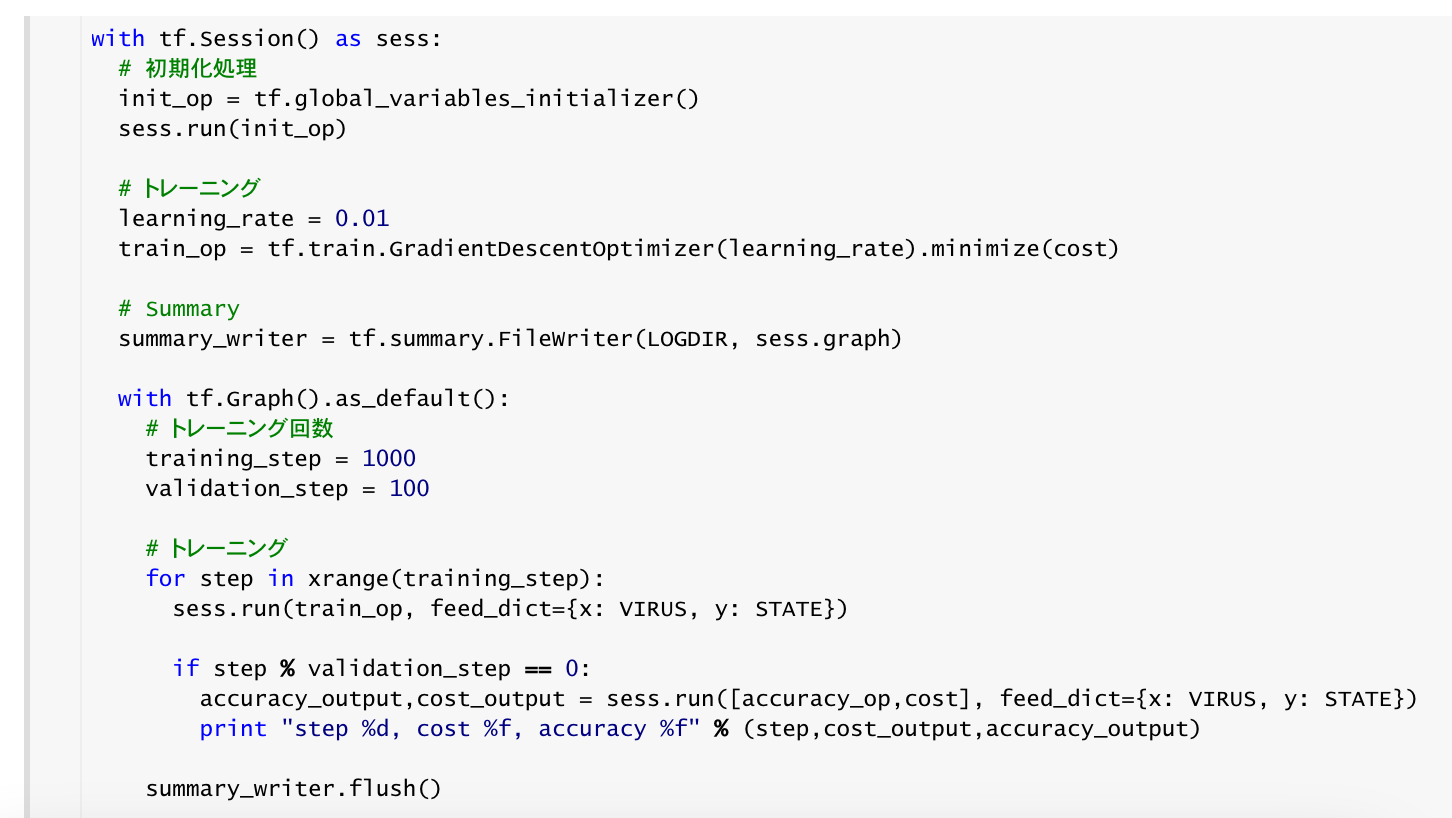
セッション内で初期化をし、学習を実施する。
Coding
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# TensorFlow r1.0.0
# Python 2.7.6
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
x_positive = np.random.randn(500, 1) + 2
y_positive = np.random.randn(500, 1) + 2
x_negative = np.random.randn(500, 1) - 2
y_negative = np.random.randn(500, 1) - 2
plt.figure(1)
plt.plot(x_positive, y_positive, 'ro', label='Data1')
plt.plot(x_negative, y_negative, 'bo', label='Data2')
N = len(x_positive)
POSITIVE = np.zeros((N,2))
for i in xrange(N):
POSITIVE[i][0] = x_positive[i]
POSITIVE[i][1] = y_positive[i]
NEGATIVE = np.zeros((N,2))
for i in xrange(N):
NEGATIVE[i][0] = x_negative[i]
NEGATIVE[i][1] = y_negative[i]
VIRUS = np.vstack([NEGATIVE, POSITIVE]).astype(np.float32)
print VIRUS
STATE = np.zeros((N*2,2), dtype=np.float32)
for i in xrange(N*2):
if i < N:
STATE[i][1] = 1
else:
STATE[i][0] = 1
print STATE
tf.reset_default_graph()
LOGDIR = "./data_virus"
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None,2), name="input")
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=(None,2), name="output")
w = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2,2], stddev=0.01), dtype=tf.float32, name="weight")
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2], stddev=0.01), dtype=tf.float32, name="bias")
# ロジスティック回帰のモデルを定義
with tf.name_scope('forward'):
y_pred = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,w) + b, name="forward")
# コストの計算
with tf.name_scope('cost'):
loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=y_pred)
cost = tf.reduce_mean(loss, 0)
# 精度の計算
with tf.name_scope('accuracy'):
correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_pred,1), tf.argmax(STATE,1))
accuracy_op = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32))
# TensorBoardへの反映
w_graph = tf.summary.histogram("W_graph", w)
b_graph = tf.summary.histogram("b_graph", b)
y_graph = tf.summary.histogram("y_graph", y)
cost_graph = tf.summary.scalar("cost_graph", cost)
with tf.Session() as sess:
# 初期化処理
init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess.run(init_op)
# トレーニング
learning_rate = 0.01
train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(learning_rate).minimize(cost)
# Summary
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(LOGDIR, sess.graph)
summary_op = tf.summary.merge_all()
with tf.Graph().as_default():
# トレーニング回数
training_step = 1000
validation_step = 100
# トレーニング
for step in xrange(training_step):
sess.run(train_op, feed_dict={x: VIRUS, y: STATE})
if step % validation_step == 0:
accuracy_output,cost_output = sess.run([accuracy_op,cost], feed_dict={x: VIRUS, y: STATE})
print "step %d, cost %f, accuracy %f" % (step,cost_output,accuracy_output)
# TensorBoardにも反映
summary_str = sess.run(summary_op, feed_dict={x: VIRUS, y: STATE})
summary_writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
summary_writer.flush()
TensorBoard
TensorBoardは、どんどんデータが蓄積されているくので、TensorFlowの学習前に、data_virusフォルダを削除する。
!rm -r ./data_virus
TensorBoardを起動する。TensorBoardは、DatalabではTensorBoardをForegroundでしか実行できないため、停止する場合は、メニューの[Reset Session]のResetで停止する。
!tensorboard --logdir=data_virus/
docker環境でtensorboardを利用するには6066ポートへのトンネルも必要 docker run -it -p 6006:6006 -p 8888:8888 tensorflow/tensorflow






Notebook
https://github.com/FaBoPlatform/TensorFlow/blob/master/notebooks/virus02.ipynb